Cyber Attacks Have Become Pervasive
There are three World Wide Webs – the Surface Web which most people browse, the Deep Web which is the hidden purview of businesses, governments, institutions and cyberhackers of the contained Dark Web. The current outbreak of cyber-crime plus malicious hacking is based in the Dark Web portion of the nearly invisible Deep Web. And the irony is that the Deep Web which was designed to harbor and protect vast amounts of confidential military, government and private information with its untraceable pathways – has become the hideout for hackers and cyber-criminals. Worse these criminals are using software created by the US Government and privacy freedom activists which allows the cyber criminals to setup shop in the Dark Web using Darknet routines to threaten and exploit the broader Surface and Deep Web information safe havens.
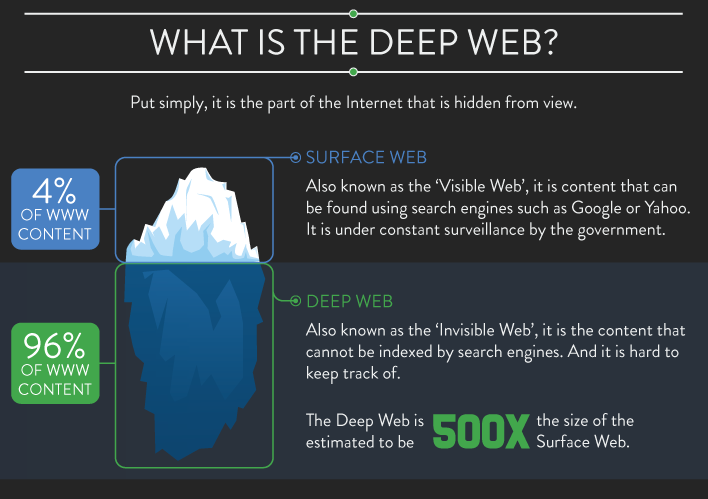 What is not shown in the chart is the size of the Dark Web part of the Deep Web. And that is because the full extent of both the Deep Web and Dark Web are both kept fiercely hidden. But the effects of the Dark Web are known by hacking intrusions, ransomware, and DDOS [Distributed Denial Of Service] attacks. And in case there is any doubt about the size and nature of the Dark Web disease consider the independent reports by IBM, CNBC, Forbes, and Accenture on the annual direct cost [$450B]and impact [$3,000B]of CyberCrimes in 2017. Other security observers like the Herjavec Group are even more strident:
What is not shown in the chart is the size of the Dark Web part of the Deep Web. And that is because the full extent of both the Deep Web and Dark Web are both kept fiercely hidden. But the effects of the Dark Web are known by hacking intrusions, ransomware, and DDOS [Distributed Denial Of Service] attacks. And in case there is any doubt about the size and nature of the Dark Web disease consider the independent reports by IBM, CNBC, Forbes, and Accenture on the annual direct cost [$450B]and impact [$3,000B]of CyberCrimes in 2017. Other security observers like the Herjavec Group are even more strident:
Cybercrime is the greatest threat to every organization in the world, and one of the biggest problems for mankind. The impact on society is reflected in the numbers. Last year, Cybersecurity Ventures predicted that cybercrime will cost the world $6 trillion annually by 2021, up from $3 trillion in 2015. This represents the greatest transfer of economic wealth in history, risks the incentives for innovation and investment, and will be more profitable than the global trade of all major illegal drugs combined.
These are staggering numbers but worldwide organizations saw a clearly visible increase in Cyberbreaches of 27.4% in 2017. Or consider the hundreds of thousands of users who got hit by Ransomware virus attacks in the year.
The Nature of the Dark Web Beast
Now it is important to understand the difference between the Surface or Visible Web versus the Deep Web. The Surface Web is what you are using now to view this post. The Deep Web contains all the networks and data nodes that want to remain private and only known to and accessible by a strictly limited set of clients.
The Surface Web has 5 characteristics:
- it is comprised of billions of indexed and known IP addresses or endpoints pointing to website contents;
- each IP address has a port which identifies whether a message has a destination address matching the IP;
- the content at the website address may or may not be encrypted, may or may not be entered without logon, and may or may not be completely indexed and stored by a 3rd party [think Google or Bing] . If indexing was allowed, then summaries of a web page’s content can be provided by search engines[again, think Google or Bing];
- the path to the website is open and can be readily traced and logged;
- and your identity as a user of the website is readily known and easily logged.
So the important point is that on the Surface Web, how to get to a website, its website contents and you as a user of the website are all publicly known, actively traced and constantly logged with or without your permission. When you see those notices of cookies policy as you enter a website, by entering you have given permission to the website owner to track any or all of your activities on the website. Now your visibility on the Surface Web can be controlled and modulated. Thus begins a necessary and helpful sidetrip useful in understanding the nature of both the Deep and Dark Web.
Controlling Your Surface Web Visibility
For website owners, entry can be limited by stricter logon requirements. Content can be encrypted redoubling the security of stored information. Finally, SSL encrypted websites [look for the green https in the URL] ensures that all data sent to and received from that website will be encrypted and much less vulnerable to hack attack.
Still privacy and anonymity is at issue because all this encryption does not prevent the browser vendor, ISP-Internet Service or the website owner from recording any or all the transactions that took place on any one of your website visits. This issue of privacy and anonymity is becoming a concern with more users seeking to restrict invasion of privacy.
Here is what users can do to insure better privacy, anonymity as well as security as they surf the Web. Access the Web using a VPN-virtual private network which provides encryption of all messages, tunneling onto the Web such that your usage of the web cannot be effectively traced, and disguising of your IP address so your identity on the Web is also hidden.
What makes a VPN effective is that it has thousands of relay servers [typically in the 2,000 to 9000 range spread all over the world]. The more relay servers, the faster the speed of the VPN and the reduced chance of unwanted exposure by traffic analysis. So what are the best VPNs and what do they cost? Well there at least 50 free and premium VPNs. The free VPNs often have monthly bandwidth maximums and some feature limitations. The premium VPNs also vie with one another with add-on features and prices ranging from $3 to $15US/month. See here for a review of the top VPNs.
So why do you have to pay to have secure browsing? Why doesn’t the browser vendor provide this VPN level of privacy? Well they pretend to by offering incognito or privacy mode of service which cuts off storing browsing activities in the local web cache and cookies. However, the ISP doing the transmission and the browsed web server are still at liberty and do store your IP address and browsing activities. The bottom line is that all three “service providers” make money by selling your browsing activities to advertisers.
So what alternatives do users have for browsing the web securely and not have to pay a VPN toll. Think Tor or I2P which are both free and have some striking common characteristics: 1)Both have thousands of their own connected relay servers scattered over the world; 2)Both use their own protocols [Tor uses onion routing, I2P uses garlic routing ]to transmit encrypted messages between relay servers such that it is impossible to trace the route or the identity of the user; 3)Both have exit relays servers that allow accessing the Surface Web. This mechanism provides VPN-like encryption plus route traversed/location invisibility for using the Surface Web. In addition, both provide better user anonymity than VPNs but are slower when browsing the Surface Web; 4)Both are, along with Freenet, open source software; 5)Both along with Freenet constitute the core of the Darknet.
So now you now why we took this sidetrip into VPNs, Tor, I2P and Freenet.
So here is the terrible truth. The same Open Source Web Network tools that provide identity and location anonymity, browsing privacy, and secure message encryption have been pirated by criminals and hackers. They either use directly Tor, I2P, or Freenet or the criminals adapt and customize these tools to be used in their own hacker Darknets for their malicious ends. So the tools that provide ordinary users with enhanced security and whistleblowers with privacy and women evading stalkers better protection and citizens of repressive regimes an uncensored glimpse of the real world – these same tools have become the tools of choice for hackers and criminals of the Dark Web.
Deep into the Dark Web
In contrast to the Surface Web, the Deep Web is deliberately hidden. When first developed the idea was to allow private and confidential data stored by government and business organization to be hidden from all but a select few using specialized peer-to-peer networks and transmission processes. So the Deep Web has the following characteristics: 1)it is comprised of thousands private network relay servers; 2)it uses networking software tools that carefully and legally disguise users’ identity, location, message content and network end destination; hence it is an invisible net with no Google-like indexing of its websites; 3)it is often based on open source software customized for specific tasks both licit and illicit: 4)among illicit tasks on the Dark Web portion of the Deep Web are marketplaces for child sex, slave trade, money laundering, arms sales, hacking software, stolen credit cards and criminal engagement. But perhaps the most serious are hacking command and control centers. These control centers deploy Botnets to carry out DDOS attacks, Ransomware strikes, spear-fishing raids, Twitter/Facebook smear campaigns and other criminal acts.
Enter our final piece of the Web Security Puzzle – Botnets
Dark Botnets are a cluster of computers all of which have been infected by a specific virus that has installed a program that lies dormant awaiting a message to commence some hack attack over the Internet. The success of a botnet relies on 4 things: 1)the computer is continually connected to the Web; 2)because of a lax firewall security and/or non-updated operational programs; the computer has been successfully invaded by a virus that installs a botnet infection app that awaits scans for a signal to unleash some attack program that will deploy over the Internet; 3)relies on the computer remaining connected to the Net, not being monitored closely for web usage and not being scanned for viruses; 4)has the ability to hide activity using either client-server or peer-to-peer messaging using an array of standard communication protocols [IRC, HTTP, SMTP, Telnet] for taking commands, scouting for fellow bots for updating themselves, and launching attacks; The botnet infection apps have become so sophisticated that a)they lie low minimizing any effects on the computers regular operations; b)they disguise themselves hiding in ignored parts of storage and c)can disable some anti-virus programs prolonging their stay. Botnets are used extensively for a wide variety of incursions: – DDOS-Distributed Denial of Service attacks designed to overwhelm a targeted server with hundreds of thousands of service requests – Spam attacks designed to breakthrough using spear fishing or spoofing to infect targets as new bots; – scouting forays designed to identify machines vulnerable for later attacks; – infiltration attacks for data theft in industrial espionage or valuable financial account or identity theft; – the range and sophistication of attacks and their self defense mechanisms is intimidating. The resulting Cyber attackers are like Cerberus, the three headed Mad Dog guarding the Depths of the River Styx. Three groups of Malicious Actors now wreak increasing havoc across the Internet. Their mode of operation is common. Thus 90% of eMail traffic is spam, and of that 10-12% is malicious phishing or spoofing which helps create massive bot networks which dominate Internet traffic [see graphic below] and helped spawn growing DDoS attacks and the spiking of ransomware to 638million attacks worldwide in 2016. 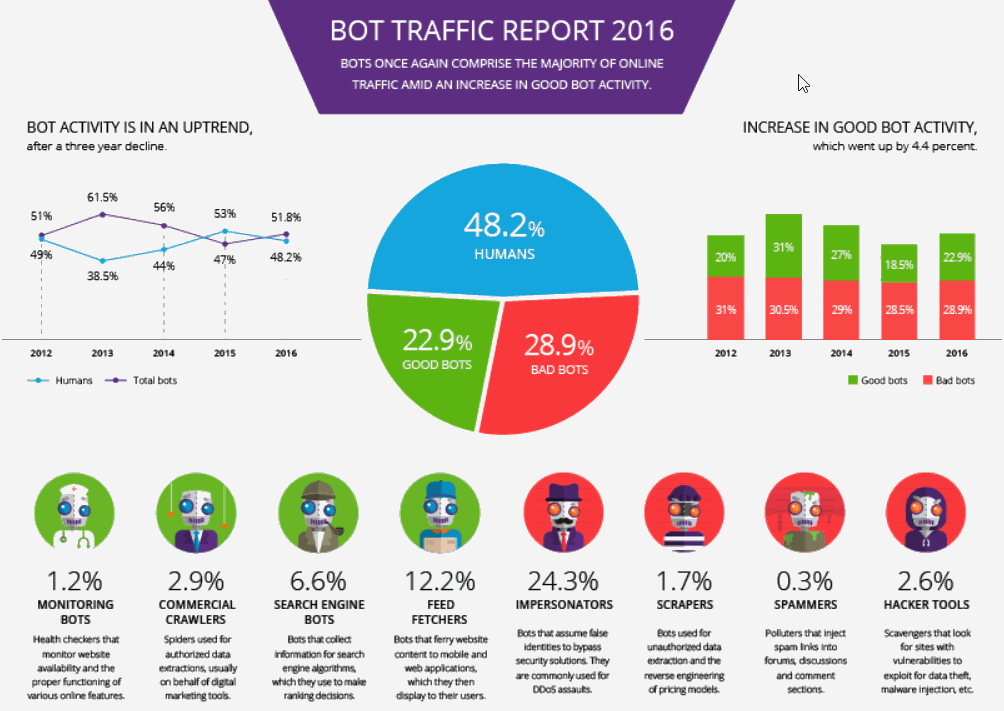
The main Cyber-Cerberus Head is the collective dark actions of Nation States. Countries like China, Russia, North Korea, Iran, Israel, USA and others use cyber attacks for massive economic espionage, political sabotage and military advantage. These Nation States now house the armories for creating ever more potent hacking tools. And even worse, a bungling US Government National Security Agency and the CIA have lost many of their ultra-secret hacking tools which have been released to the DarkWeb and the broader Hacking Marketplace.
In the past ten years, the second Cyber-Cerberus head has emerged – hacking has become a highly profitable business as underlined by the Economist and a chilling report on the extent and cost of hacking vulnerability by Lloyds of London Insurance. For example, revenues just from hacking Bitcoin and other blockchain-based currency hacks have been topping $200 million/year and 2018 has already seen Bitcoin looting exceeding $150 million in the first month. But this is just the tip of activities on the Dark Web where Tor browsing ensures anonymity for criminal hackers to diverse cyber markets like hacking software suites, bitcoin hackers, ransomware vendors, money laundering shops, stolen identification retailers, and espionage hacking contractors. This is the Dark Web. These criminal hackers are now armed with sinister AI tools for rapidly identifying vulnerable targets To repeat Herjavec’s warning, crypto-looting has become a huge and highly profitable criminal business worth hundreds of billions every year.
The third Cyber-Cerberus Head is Hacktivism – the use of computer tools to promote social change or a political agenda. Hacktivism has brought a patina of legitimacy to Hacking and Cyber-attacks. The Dark Web is justified by Hacktivists as the only place you can go and not be tracked/traced by government and corporates. The end is purported to be safe traversing of the Web. But hacktivist organizations such as Anonymous, LulzSec, and Wikileaks are now employing ever more potent hack tools in their causes. In effect they are using and therefore promoting the methods and markets of the DarkWeb. But the worst part is that hacking and cyber-criminals flourish due to simple organizational negligence.
Cyberattacks Thrive on Negligence
For every cunning cyber attack dependent on using clever code infections, SQL injection, or cross site trojans there are countless more breaches dependent on easy entry: simple passwords, unprotected web connections, and systems left without updates. Hackers thrive on getting into unprotected systems by the easiest path possible – looking for open doors on sucker systems. And now there are more hacking tools that automate the process of identifying sucker systems and their weaknesses.
But two other factors contribute to the rise of Cyber hack attacks. First, the rate of disruptive change on the Web has accelerated. The Internet sales are now putting more brick and mortar businesses on the ropes. So computer automation is being used everywhere as seen with mobile phones, automated vending, and smart devices. This is the basis for the IoT – the Internet of Things which truly bring convenience but quietly open users to cyber attacks.
The second factor increasing Cyber vulnerability is the rapid rate of change in software. As a programmer I now see updates on bimonthly basis across a whole range of programs and systems. And I know that many of those updates are essential for closing hack attack weaknesses in the software as well as bug fixes and improvements. Thus keeping up with critical updates is a vital ; but failure to do so has consistently been the cause of huge data breaches.
So this is why the latest Cisco Security Report is relevant. They have an infographic depicting the scrambled state of affairs in Cyber Security efforts in large organizations:  Cisco state its case in simple upfront language:
Cisco state its case in simple upfront language:
“You can’t defend against threats you don’t address. With 44% of security alerts never being investigated, organizations need simple and more effective solutions.”
So here is what Cisco describes as key concerns in Cyber Security given Hacker attack modes:
● Taking advantage of lapses in patching and updating ● Luring users into socially engineered traps ● Injecting malware into supposedly legitimate online content such as advertising ● Identifying highly susceptible web targets
The result is that there is a continuing stream of large scale data breaches: 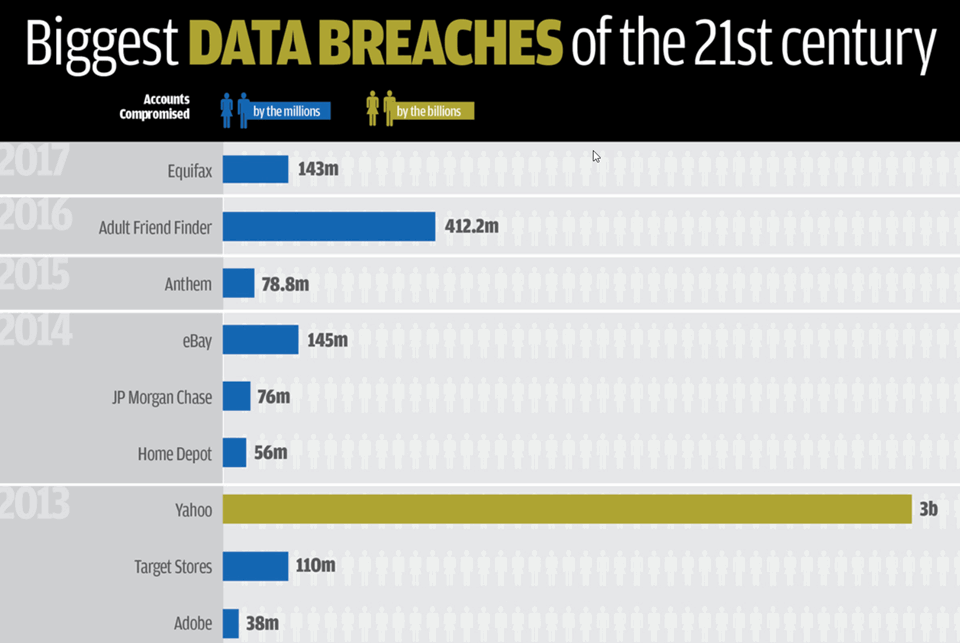 These large breaches provide hackers with rich resources for dark web sales of vital personal information. Worse some vendor like Yahoo continue to fall prey to hack attacks with an added 32 million lost accounts in the last 2 years. The result is that hackers are now using the best US Crypto-tools for attacking business and government agencies worldwide – and especially small businesses.
These large breaches provide hackers with rich resources for dark web sales of vital personal information. Worse some vendor like Yahoo continue to fall prey to hack attacks with an added 32 million lost accounts in the last 2 years. The result is that hackers are now using the best US Crypto-tools for attacking business and government agencies worldwide – and especially small businesses.
Cyber-security threatens small business
Many small business organizations consider themselves too small for cyber-attacks. This is definitely the wrong notion as described by Cisco, Inc Magazine, USA Today, and Ponemon Institute. The increase in cyberattacks on small business reached a new high in 2017 – over 55% 0f small businesses experienced an attack in the last year. The other data for small business vulnerability to cyber attacks is compelling: – 61% of breaches hit smaller businesses last year, up from the previous year’s 53%; – Cyber attacks cost small businesses between $84,000 and $148,000; – 60% of small businesses go out of business within six months of an attack; – 90% of small business don’t use any data protection at all for company and customer info; – Thus, cyber-criminals prefer small business as soft targets: 1)small businesses will pay ransoms: 2)small businesses have easily accessible financial and identity data; 3)small businesses make it easier to infiltrate other businesses; 4)many small businesses lack basic cyber defenses; 5)It is easier to get away with attacks on small business versus larger corporates; – 14 million small businesses in the US were breached last year; – yet 82% of small business managers do not feel that they’re at risk for cyberattack.
So small business, government and non-profit sites are increasingly targeted by cyber attackers. And our own survey of the 517 CSI small business websites uncovered another serious vulnerability. 61% of the CSI websites had not been updated in the last 3 months and over 20% had not been updated in a year – just the kind of website target with obsolete software the cyber-hackers are looking for.
Yet there are low cost yet highly effective means for improving small business security: 1)do monthly website backups of data and programming storing the backups offsite; 2)make your website SSL protected so all transactions are encrypted and not subject to spoofing and snooping; 3)use a VPN for all online usage affording major step up in Web transaction security; 4)use a firewall to protect your computer against hack attacks and email spam, the most frequent methods for hacking into your systems; 5)have a security status meeting quarterly with all employees using systems or the Web attending and reporting any anomalies. Having helped mop up 3 hack attacks in the past year I can testify that these methods work.
Summary
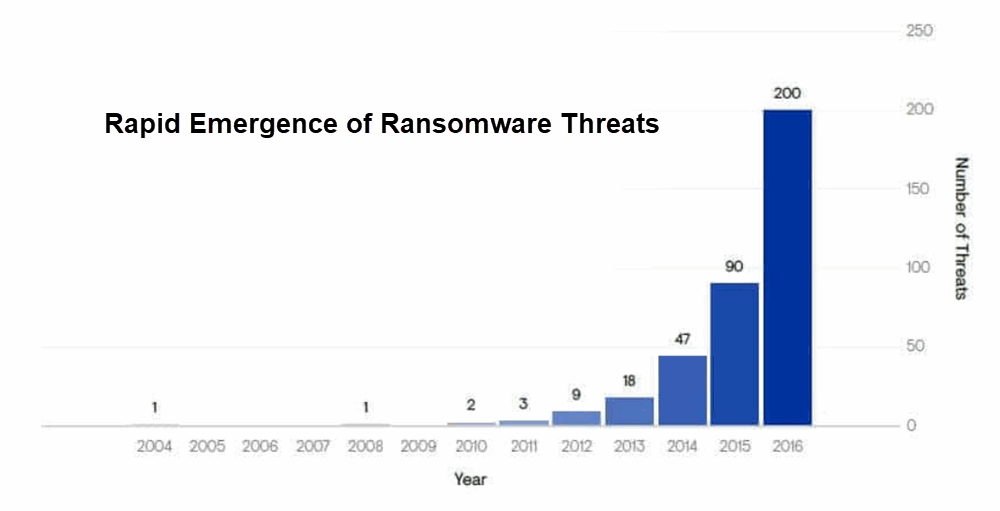 Cyber attacks have increased steadily for the past ten years such that a nuisance has become a crisis. The chart above shows the latest hockey stick growth in cyberattacks – in this case Ransomware variants The productivity of the Web is threatened by relentless attacks by three major players – Nation States conducting ever more consequential cyberwars and helping arm the other two cyber players – Organized Cyber-Criminals and Cyber-Hacktivists.
Cyber attacks have increased steadily for the past ten years such that a nuisance has become a crisis. The chart above shows the latest hockey stick growth in cyberattacks – in this case Ransomware variants The productivity of the Web is threatened by relentless attacks by three major players – Nation States conducting ever more consequential cyberwars and helping arm the other two cyber players – Organized Cyber-Criminals and Cyber-Hacktivists.
It is the Cyber-Criminals who for the past three years with Botnet armies of millions have threatened every part of systems operations for organizations both large and small throughout the World. This the challenge faced by web users throughout the World.
Fortunately, there is a number of simple mechanisms available to Web User and website owners to provide much enhanced protection for their information tools and assets. For individuals on their PCs and mobile devices it is 4 main protective methods: 1)Use a VPN when surfing the Web for much enhanced message security and surfing privacy; 2)Have a firewall to block hack attacks and screen out email spam-based viruses; 3)do backups of data and valued resource to off-device storage; 4)Be aware that criminals now use the Web and messaging more than physical criminal acts. So act accordingly.
For small business website owners think differently about using the Web. Now when there is more cyber risk there are advantage to using SaaS-Software-as-a-Service providers and other Cloud Container Services like AWS-Amazon Web Services and Azure. These services remove all the worries about having the latest system updates, doing proper back-up and recovery operations while providing enhanced security against cyberattacks and even performance tuning with adaptive response to traffic spikes/valleys in usage.
The trade-off is that these SaaS tools may not provide the add on features, layout/styling control and design customization desired. They also can be more costly. These two factors apply in the case of SaaS Web Builder’s like Magento, Shopify, SquareSpace, Wix, Weebly, WordPress.com and Zoho. Also be sure to factor in some substantial learning curves for these tools.
For DIY websites tools JavaScript Frameworks, Drupal, Joomla and WordPress offer huge libraries of layout themes, interactive PageBuilders and operational plugins that guarantee you can build your custom design and functional system. But these systems will require more backend refinement. First, the hosting service should provide SSL encryption, automatic backup and recovery services on conditional settings, caching for performance tuning plus a basic firewall against virus attacks and for spam control. Depending on the hosting service these settings may be automated or require user action.
Then after the website software is installed [typically JavaScript Framework or WordPress], then the user installs plugins [most are free] to complete the security setup, enhance the performance tuning, add SEO refinements, do special backup/recovery/website migration and track the website usage statistics.
So the trade-off is as follows: SaaS based systems automate much of the setup and web security work where as the the user/developer is required to carry out the hosting service setup and website software installation. It is an opportunity to complete the setup such that web security is maximized. For this extra effort, one can get a better overall level of security and performance than in the case of SaaS systems.
The bottom line is that hackers are getting better while Web users are still not in the game. So that the growing threat of cyber attacks puts more pressure on web users as well as website owners, especially for small organizations, to devote more energy in planning their Web security all the time and everywhere the Web take them. Not just their website and browsing but all their user connections must be fortified for the continuing onslaught from the Dark Web’s cyber criminals.
